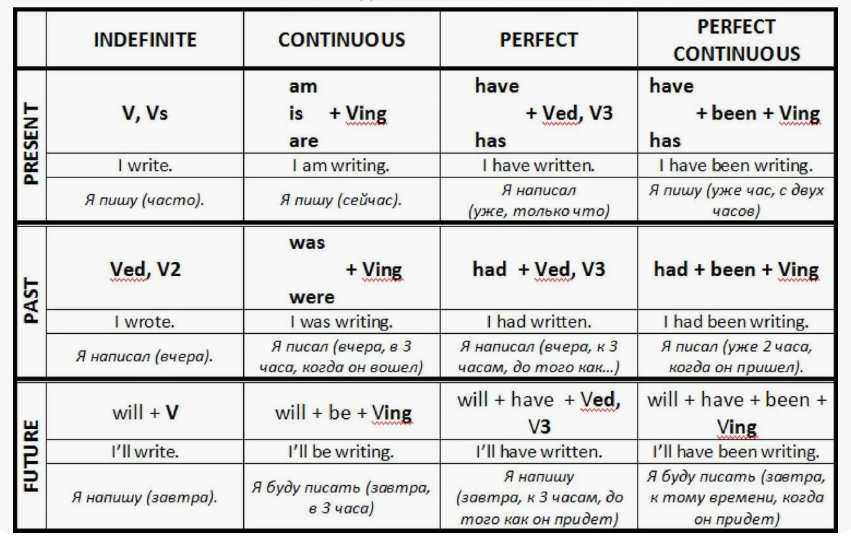
В английском языке существует несколько времен, используемых для выражения разных видов действий и состояний. Основные группы:
- Времена группы Present
- Времена группы Past
- Времена группы Future


Present Simple (Настоящее простое время)
| Выражает регулярные действия, общие факты и состояния. Также используется для расписаний. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + основная форма глагола (основной формы глагола, добавив "-s" или "-es" для третьего лица единственного числа).
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + do/does (в зависимости от лица) + not + основная форма глагола.
- Вопросительные предложения: Do/Does (в зависимости от лица) + субъект + основная форма глагола?
Примеры:
- I play the piano.
- He doesn't like coffee.
- The plane takes off at 7 PM.
- Do you speak English?
Слова-маркеры:
always, usually, often, sometimes, every day/week/year etc., seldom, rarely, regularly, never.
Present Continuous (Настоящее длительное время)
|
Выражает текущие действия, происходящие в момент речи. Также используется для планов.
|
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + to be (в соответствии с лицом) + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + to be (в соответствии с лицом) + not + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Вопросительные предложения: To be (в соответствии с лицом) + субъект + основная форма глагола + -ing?
Примеры:
- She is reading a book at the moment.
- I'm not going abroad this spring.
- Are you listening to music now?
Слова-маркеры:
now, at present, at the moment, look!, listen!, this summer/year/month etc., tonight, currently, right now.
Present Perfect (Настоящее совершенное время)
| Связано с прошлыми событиями, имеющими отношение к настоящему. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + have/has (в соответствии с лицом) + основная форма глагола (3-я форма).
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + have/has + not + основная форма глагола (3-я форма).
- Вопросительные предложения: Have/Has + субъект + основная форма глагола (3-я форма)?
Примеры:
- Have you ever been to Paris?
- She has visited Rome twice.
- The teacher hasn't checked the tests yet.
Слова-маркеры:
already, just, yet, still, ever, never, before, recently, lately.
Present Perfect Continuous (Настоящее совершенное продолженное время)
| Выражает действия, начавшиеся в прошлом и продолжающиеся в настоящем. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + have/has (в соответствии с лицом) + been + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + have/has + not + been + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Вопросительные предложения: Have/Has + субъект + been + основная форма глагола + -ing?
Примеры:
- He has been working here for five years.
- They haven't been waiting long.
- Have you been playing the guitar?
Слова-маркеры:
for, since, all evening/week/day etc., recently.
Past Simple (Прошедшее простое время)
|
Описывает завершенные действия в прошлом.
|
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + основная форма глагола (2-я форма).
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + did + not + основная форма глагола.
- Вопросительные предложения: Did + субъект + основная форма глагола?
Примеры:
- She visited London last summer.
- Yesterday I didn't buy a new car.
- Did they enjoy the concert?
Слова-маркеры:
yesterday, last week/month/year etc., in 2009, in the past, ago, the day before yesterday, the other day, in the 90s etc.
Past Continuous (Прошедшее продолженное время)
| Описывает действия, которые происходили в определенный момент в прошлом. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + was/were (в соответствии с лицом) + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + was/were + not + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Вопросительные предложения: Was/Were + субъект + основная форма глагола + -ing?
Примеры:
- They were playing tennis at 5 o'clock yesterday.
- She wasn't sleeping when I called.
- Were you studying when the phone rang?
Слова-маркеры:
at N o'clock, at N o'clock last week/mont etc., all night long, at lunchtime, from 2 till 4, when, while.
Past Perfect (Прошедшее совершенное время)
| Указывает на события, произошедшие до других событий в прошлом. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + had + основная форма глагола (3-я форма).
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + had + not + основная форма глагола (3-я форма).
- Вопросительные предложения: Had + субъект + основная форма глагола (3-я форма)?
Примеры:
- By the time we arrived, they had already left.
- She hadn't eaten breakfast before she left.
- Had you ever visited Paris before this trip?
Слова-маркеры:
before, by that time, by N o'clock, after.
Past Perfect Continuous (Прошедшее совершенное продолженное время)
| Описывает действия, которые продолжались в прошлом и имеют отношение к другим моментам времени. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + had + been + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + had + not + been + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Вопросительные предложения: Had + субъект + been + основная форма глагола + -ing?
Примеры:
- She had been working for hours before she took a break.
- They hadn't been waiting long when the bus arrived.
- Had you been studying for a long time before the exam?
Слова-маркеры:
before, till, until, since N o'clock/last summer/2002 etc., for an hour/week/year, all/the whole day/morning/month etc.
Future Simple (Будущее простое время)
| Используется для выражения будущих действий или событий. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + will + основная форма глагола.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + will + not + основная форма глагола (или сокращенно - won't).
- Вопросительные предложения: Will + субъект + основная форма глагола?
Примеры:
- She will call you later.
- I won't be able to attend the meeting.
- Will you help me with this task?
Слова-маркеры:
tomorrow, soon, later, as soon as, next week/month/year etc., in a month.
Future Continuous (Будущее продолженное время)
| Выражает действие, которое будет продолжаться в определенный момент в будущем. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + will + be + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + will + not + be + основная форма глагола + -ing (или сокращенно - won't be).
- Вопросительные предложения: Will + субъект + be + основная форма глагола + -ing?
Примеры:
- At this time tomorrow, I will be studying for my exam.
- They won't be working on the project next week.
- Will you be attending the conference?
Слова-маркеры:
this time tomorrow, during that time, from 2 till 4, at that moment, at N o'clock, next.
Future Perfect (Будущее совершенное время)
| Указывает на события, которые будут завершены к определенному моменту в будущем. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + will + have + основная форма глагола (3-я форма).
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + will + not + have + основная форма глагола (3-я форма) (или сокращенно - won't have).
- Вопросительные предложения: Will + субъект + have + основная форма глагола (3-я форма)?
Примеры:
- By next year, I will have graduated from university.
- She won't have finished the report by the deadline.
- Will you have completed the project by Friday?
Слова-маркеры:
till, untill, for, by the time, before, by
Future Perfect Continuous (Будущее совершенное продолженное время)
| Описывает действия, которые будут продолжаться до определенного момента в будущем. |
- Утвердительные предложения: Субъект + will + have + been + основная форма глагола + -ing.
- Отрицательные предложения: Субъект + will + not + have + been + основная форма глагола + -ing (или сокращенно - won't have been).
- Вопросительные предложения: Will + субъект + have + been + основная форма глагола + -ing?
Примеры:
By the time you arrive, I will have been waiting for an hour.
They won't have been living in the city for long by the end of the year.
Will you have been studying for a long time before the test?
Слова-маркеры:
till, untill, for, by the end of the hour/day/morning etc.
Тест по теме “Активные времена в английском языке”
Разбор:
Набранные баллы:
9
Смотреть разбор
Отправить тест на проверку?
Ты решил еще не все задания